เนื่องจากระยะเวลาการให้ยาต้านเกล็ดเลือดร่วมกัน (Dual antiplatelet therapy, DAPT)ในผู้ป่วยที่มีความเสี่ยงสูงต่อภาวะเลือดออกภายหลังการขยายหลอดเลือดหัวใจด้วยบอลลูนและใส่ขดลวด (Percutaneous coronary intervention, PCI)ยังไม่ชัดเจน นำมาสู่งานวิจัยนี้ซึ่งสุ่มผู้ป่วยที่ได้รับการผ่าตัดใส่ biodegradable-polymer sirolimus-eluting coronary stent นานราว 1 เดือน (30-44 วัน, median = 34 วัน) ออกเป็น 2 กลุ่ม ในอัตราส่วน 1:1 ได้แก่
- Abbreviated therapy:
- กรณีไม่ได้รับ oral anticoagulant (OAC) ร่วมด้วย: หยุด DAPT ทันที ตามด้วย single antiplatelet therapy (SAPT) อย่างน้อย 11 เดือนหลังการสุ่ม
- กรณีได้รับ OAC ร่วมด้วย: หยุด DAPT ทันที ตามด้วย aspirin หรือ clopidogrel 5 เดือน โดยได้รับ OAC ครบ 12 เดือน หลังทำ PCI
- Standard therapy:
- กรณีไม่ได้รับ OAC ร่วมด้วย: ได้รับ DAPT (aspirin และยากลุ่ม P2Y12 inhibitors) ต่อ 5 เดือน ตามด้วย 2 กรณี คือ
- ได้รับ aspirin อย่างเดียวต่อจนครบ 12 เดือนหลังทำ PCI
- ได้รับทั้ง aspirin และ P2Y12 inhibitors ต่อไม่เกิน 12 เดือนหลังทำ PCI
- กรณีได้รับ OAC ร่วมด้วย: ได้รับ DAPT (aspirin และ clopidogrel) ต่อ 2 เดือน ตามด้วย 2 กรณี คือ
- ได้รับ aspirin หรือ clopidogrel อย่างเดียวต่อจนครบ 12 เดือนหลังทำ PCI โดยได้รับ OAC ครบ 12 เดือน หลังทำ PCI
- ได้รับทั้ง aspirin และ clopidogrel ต่อไม่เกิน 12 เดือนหลังทำ PCI โดยได้รับ OAC ครบ 12 เดือน หลังทำ PCI
- กรณีไม่ได้รับ OAC ร่วมด้วย: ได้รับ DAPT (aspirin และยากลุ่ม P2Y12 inhibitors) ต่อ 5 เดือน ตามด้วย 2 กรณี คือ
ในงานวิจัย อายุเฉลี่ยของผู้ป่วยเท่ากับ 76 ปี ร้อยละ 69.3 เป็นเพศชาย ร้อยละ 36.2 เป็นผู้ป่วยที่ได้รับ oral anticoagulant ร่วมด้วย และร้อยละ 48.3 ได้รับการทำ PCI สำหรับ acute coronary syndrome โดยผู้ป่วยมีคุณสมบัติตรงเกณฑ์ประเมิน high bleeding risk เฉลี่ยต่อผู้ป่วยเป็น 2.1±1.1 ข้อ (จากทั้งหมด 10 ข้อ)
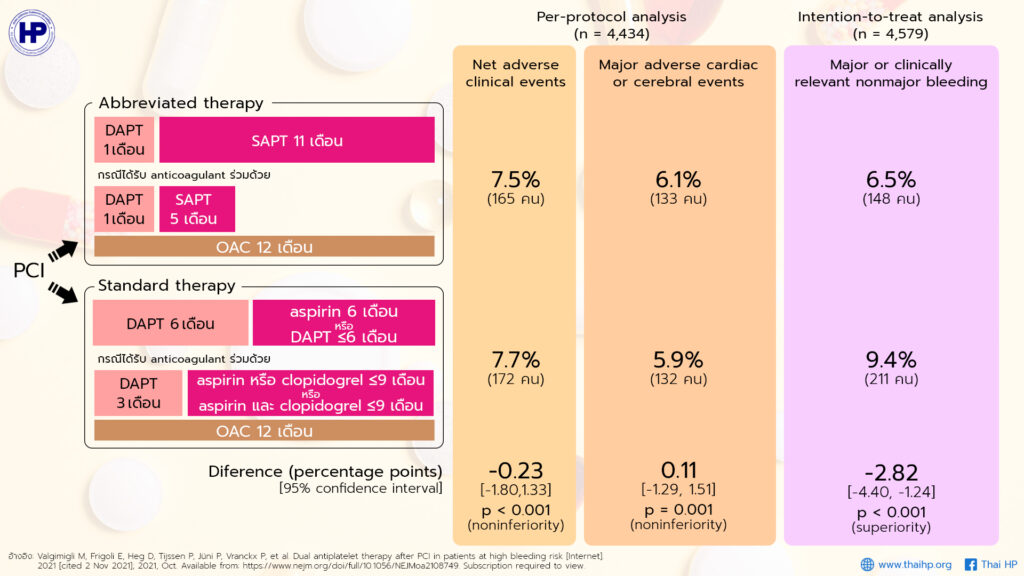
พบว่า primary outcome ที่ประเมินจาก cumulative incidence ในวันที่ 335 (± 14 วัน) เป็นดังนี้
- Net adverse clinical events (composite of death from any cause, myocardial infarction, stroke, or major bleeding) วิเคราะห์จากข้อมูลผู้ป่วย 4,434 คน (per-protocol population)
- Abbreviated therapy: 165 คน (7.5%)
- Standard therapy: 172 คน (7.7%)
- Difference, -0.23 percentage points; 95% confidence interval [CI], -1.80 to 1.33; p<0.001 for noninferiority
- Major adverse cardiac or cerebral events (composite of death from any cause, myocardial infarction, or stroke) วิเคราะห์จากข้อมูลผู้ป่วย 4,434 คน (per-protocol population)
- Abbreviated therapy: 133 คน (6.1%)
- Standard therapy: 132 (5.9%)
- Difference, 0.11 percentage points; 95% CI, -1.29 to 1.51; p=0.001 for noninferiority
- Major or clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding โดยนิยามตาม Bleeding Academic Research Consortium type 2, 3 or 5 bleeding วิเคราะห์จากข้อมูลผู้ป่วย 4,579 คน (intention-to-treat population)
- Abbreviated therapy: 148 คน (6.5%)
- Standard therapy: 211 คน (9.4%)
- Difference, -2.82 percentage points; 95% CI, -4.40 to -1.24; p<0.001 for superiority
ผู้วิจัยสรุปว่า การให้ DAPT 1 เดือนในกลุ่ม abbreviated therapy ไม่ด้อยไปกว่าการให้ DAPT 3 เดือนหลังได้รับการทำ PCI เมื่อคำนึงถึงการเกิด net adverse clinical events และ major adverse cardiac or cerebral events อีกทั้งกลุ่มที่ได้รับ abbreviated-therapy ยังเกิด major or clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding ต่ำกว่าอีกด้วย
อ้างอิง: Valgimigli M, Frigoli E, Heg D, Tijssen P, Jüni P, Vranckx P, et al. Dual antiplatelet therapy after PCI in patients at high bleeding risk. NEJM [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2 Nov 2021]; 2021, Oct. Available from: https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2108749. Subscription required to view.

